EMSAT is a crucial examination for students aspiring to pursue higher education in the United Arab Emirates. Particularly for those tackling the chemistry section, a thorough understanding of key concepts is essential for success in the chemistry emsat practice. To help you prepare effectively, we here in ELMADRASAH.COM platform have compiled a list of the top 10 sample questions that are representative of the types of challenges you might encounter on the EMSAT chemistry exam.
Your EmSAT Chemistry Practice Test with ELMADRASAH.COM
Delving into the intricacies of the EmSAT Chemistry Sample Questions, Elmadrasa.com offers you the detailed answers that unravel the complexities of each query specific to chemistry emsat practice. As chemistry is a multifaceted subject, ranging from matter and bonding to stoichiometry and thermodynamics, a comprehensive understanding is vital for success in the chemistry emsat practice. The following responses of Elmadrasa.com offer not just the correct choices but also in-depth explanations to demystify the logic behind them. Whether you navigated through multiple-choice questions on matter or faced the challenge of drag-and-drop tasks related to analytical chemistry, these detailed answers aim to enhance your comprehension and reasoning skills in the context of EmSAT Chemistry Practice Test.
Here are the detailed answers to the varied top 10 EmSAT Chemistry Sample Questions:
Proton and Electron Charges in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice:
Compared to the charge of a proton, the electron charge is:
– A) equal and of opposite sign
– B) smaller and of opposite sign
– C) greater and of the same sign
– D) equal and of the same sign
Correct Answer: A) equal and of opposite sign
Detailed Explanation:
Both protons and electrons are subatomic particles that carry an electric charge. The charge of a proton is positive, while the charge of an electron is negative. The magnitudes of these charges are equal, but they have opposite signs. The elementary charge (denoted as “e”) is a fundamental physical constant that represents the charge of a proton or an electron. The magnitude of the charge of an electron is approximately equal to the magnitude of the charge of a proton, and they are both considered to have a charge of about -1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs (C) in the International System of Units (SI). So, in summary, the electron charge is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the charge of a proton. This fundamental property of particles plays a crucial role in the structure of atoms and the interactions between them, in the context of the chemistry emsat practice.
Chlorine Atom Electron Transition in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice:
Chlorine atom is in an excited state. When an electron in this atom jumps from the fourth to the third shell, energy is:
– A) released
– B) absorbed
– C) disappeared
– D) converted to electricity
Correct Answer: B) absorbed
Detailed Explanation:
When an electron moves from a higher energy level (shell) to a lower energy level within an atom, energy is typically released. This process is known as an electron transitioning to a lower energy state or emitting a photon. However, the question describes a scenario where the electron is moving from the fourth to the third shell in a chlorine atom that is already in an excited state. In an excited state, an electron has absorbed energy and moved to a higher energy level. If this electron then transitions back to a lower energy level within the same atom, it will need to release the absorbed energy. The energy is released in the form of a photon, which may be in the form of light or electromagnetic radiation. Therefore, the correct answer, released, as the electron, in this case, is returning to a lower energy state and releasing the excess energy it had previously absorbed when it was in the excited state, in the context of the chemistry emsat practice.
Mixture Properties in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice:
One of the most important properties of mixtures is that they ____.
– A) may have different proportions
– B) have fixed proportions of their components
– C) can be separated only by chemical means
– D) are very reactive and unstable
Correct Answer: A) may have different proportions
Detailed Explanation:
Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances physically mixed together, but not chemically combined. In a mixture, the substances involved retain their individual properties, and the proportions of the components can vary. This is a fundamental characteristic of mixtures and distinguishes them from compounds. In a mixture, the components can be present in different amounts or proportions, and these proportions can be adjusted without changing the nature of the substances involved. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform composition throughout, like a solution) or heterogeneous (non-uniform composition, like a suspension or colloid). Conversely, in a compound, the elements are chemically combined in fixed proportions according to their chemical formula. Changing the proportions of elements in a compound would result in a different substance, in the context of the chemistry emsat practice. So, one of the most important properties of mixtures is their flexibility in terms of proportions, making them versatile and allowing for a wide range of combinations.
Magnesium vs. Zinc for Cathodic Protection in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice:
The statements below explain why magnesium is preferred over zinc to protect underground iron pipes in terms of reactivity except for ____.
– A) Zinc is more active than magnesium
– B) Magnesium atoms lose electrons more easily than zinc atoms
– C) Magnesium oxidized more readily than zinc
– D) Magnesium is more active than zinc
Correct Answer: A) Zinc is more active than magnesium
Detailed Explanation:
In the context of corrosion protection, metals are often used as sacrificial anodes to prevent the corrosion of other metals. This process is known as cathodic protection. The sacrificial anode, typically made of a more reactive metal, corrodes preferentially to protect the less reactive metal. So, the correct answer is Zinc is more active than magnesium, in the context of the chemistry emsat practice, as Magnesium is preferred over zinc for cathodic protection because it is more reactive and tends to corrode sacrificially, providing better protection to the underground iron pipes.
Mass Percent in chemistry emsat practice
- Fill-in-the-Blank:
Calculate the mass percent of aluminum in the compound below. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number)
Al₂(SO₄)₃
Answer = ____%
Correct Answer: approximately 36%
Detailed Explanation:
To calculate the mass percent of aluminum in Al₂(SO₄)₃, you need to determine the molar mass of aluminum and the molar mass of the entire compound, in the context of the chemistry emsat practice.
The molar mass of aluminum (Al) is approximately 27 g/mol.
For Al₂(SO₄)₃, you need to sum the molar masses of each element present, taking into account the subscripts:
– Al₂: 2 × 27 g/mol = 54 g/mol (2 aluminum atoms)
– SO₄: 32 g/mol + (4 × 16 g/mol = 96 g/mol (1 sulfur atom and 4 oxygen atoms)
Now, add these values to find the molar mass of Al₂(SO₄)₃:
54 g/mol + 96 g/mol = 150 g/mol
Now, calculate the mass percent of aluminum:
(Molar mass of aluminum ÷ Molar mass of Al₂(SO₄)₃) × 100
(54 g/mol ÷ 150 g/mol) × 100 ≈ 36%
So, the mass percent of aluminum in Al₂(SO₄)₃ is approximately 36%.
Sublimation Equation in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice:
Which of the following equations represents sublimation?
– A) CO₂(s) → CO₂(g)
– B) Hg(l) → Hg(s)
– C) CH₃OH(g) → CH₃OH(l)
– D) CH₄(l) → CH₄(g)
Correct Answer: D) CH₄(l) → CH₄(g)
Detailed Explanation:
Sublimation is the process in which a substance transitions directly from the solid phase to the gaseous phase without passing through the liquid phase. In the context of the chemistry emsat practice, the given option: CH₄(l) → CH₄(g), this equation represents sublimation because it shows methane (CH₄) transitioning directly from the liquid (l) phase to the gaseous (g) phase. The absence of an intermediate liquid phase in this process is characteristic of sublimation. In sublimation, the substance absorbs energy to break intermolecular forces holding the solid together and transforms into a gas. The reverse process, where a substance transitions directly from gas to solid, is also considered sublimation. Therefore, CH₄(l) → CH₄(g), is the one that correctly represents sublimation.
Nuclear Reaction in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice:
Given the equation representing a nuclear reaction in which X represents a nuclide:
²³⁵U
⁹²
+
¹n
⁰
→ X
Which nuclide is represented by X?
– A) ²³⁶U
⁹²
– B) ²³⁴U
⁹²
– C) ²³⁵Np
⁹³
– D) ²³⁶Np
⁹²
Correct Answer: A) ²³⁶U
⁹²
Detailed Explanation:
The given nuclear reaction is:
²³⁵U
⁹²
+
¹n
⁰
→ X
Here, a neutron ¹n
⁰
collides with a uranium-235 ²³⁵U
⁹²
nucleus, resulting in a nuclear reaction where a new nuclide X is formed.
To find the correct nuclide X, we need to consider the conservation of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in a nuclear reaction. Uranium-235 ²³⁵U
⁹²
has 92 protons, and the neutron ¹n
⁰
contributes 1 neutron to the reaction.
The sum of protons and neutrons on the left side of the reaction must be equal to the sum of protons and neutrons on the right side. Therefore, the resulting nuclide X should have a total of 92 + 1 = 93 nucleons.
Among the given options:
- A) ²³⁶U
⁹²
This nuclide has a total of 92 + 144 = 236 nucleons, which does not match the required 93 nucleons.
- B) ²³⁴U
⁹²
This nuclide has a total of 92 + 142 = 234 nucleons, which does not match the required 93 nucleons.
- C) ²³⁵Np
⁹³
This nuclide has a total of 93 + 142 = 235 nucleons, which matches the required 93 nucleons. However, it doesn’t match the original element uranium (U).
- D) ²³⁶Np
⁹²
This nuclide has a total of 93 + 143 = 236 nucleons, which does not match the required 93 nucleons.
Therefore within the context of the chemistry emsat practice, the correct answer is ²³⁶U
⁹²
which has the correct number of nucleons (92 + 144 = 236) and retains the original element uranium (U).
Measure of Average Kinetic Energy in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following terms used as a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample?
– A) temperature
– B) pressure
– C) volume
– D) chemical energy
Correct Answer: A) temperature
Detailed Explanation:
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. In a system at a higher temperature, the particles have greater kinetic energy, meaning they move faster on average. Conversely, in a system at a lower temperature, the particles have lower kinetic energy and move more slowly on average. The kinetic theory of gases provides a conceptual framework for understanding this relationship. According to this theory, the temperature of a gas is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of its particles. Pressure (option B) is related to the force exerted by gas particles on the walls of the container, and it is not a direct measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles. Volume (option C) is a measure of the space occupied by a substance and is not directly related to the average kinetic energy of particles. Chemical energy (option D) is associated with the potential energy stored in chemical bonds and is not a measure of the kinetic energy of particles. Therefore within the context of the chemistry emsat practice, temperature (option A) is the correct term used to describe the average kinetic energy of particles in a sample.
Bonding Electrons in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice
What is the total number of electrons shared in the bonds between the two nitrogen atoms in the following molecule
H H
\ /
 C=C—N≡N—H
C=C—N≡N—H
/ \
H H
– A) 6
– B) 2
– C) 3
– D) 8
Correct Answer: A) 6
Detailed Explanation:
To determine the total number of electrons shared in the bonds between the two nitrogen atoms in the context of the chemistry emsat practice, let’s analyze the bonds in the molecule:
– There is a double bond (C=C) between the carbon atoms. A double bond consists of one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond.
– There is a triple bond (N≡N) between the two nitrogen atoms. A triple bond consists of one sigma (σ) bond and two pi (π) bonds.
So, between the two nitrogen atoms, there is one sigma (σ) bond and two pi (π) bonds.
The total number of electrons shared in these bonds is calculated as follows:
– Each sigma (σ) bond contributes 2 electrons.
– Each pi (π) bond contributes 2 electrons.
Therefore, for the bonds between the two nitrogen atoms:
– Sigma (σ) bond: 2 electrons
– Pi (π) bonds: 2 * 2 = 4 electrons
Total electrons shared = 2 (sigma) + 4 (pi) = 6 electrons.
The correct answer is A) 6.
Capacity Calculation in chemistry emsat practice
- Fill-in-the-Blank:
An elevator at shopping mall has a maximum load of 1600 lb. How many 75 kg persons can use the elevator at the same time? (1 lb = 0.45359237)
Answer = ____
Correct Answer: 9 persons
Detailed Explanation:
First, we need to convert the maximum load of the elevator from pounds to kilograms since the weight of the persons is given in kilograms, in the context of the chemistry emsat practice.
1 lb = 0.45359237 kg
So, the maximum load of the elevator in kilograms is:
1600 lb * 0.45359237 kg/lb = 725.747792 kg (approximately)
Now, we can calculate how many 75 kg persons can use the elevator at the same time:
Number of persons = Maximum load of elevator / Weight of each person
Number of persons = 725.747792 kg / 75 kg ≈ 9.676637
Since we can’t have a fraction of a person, we’ll consider only the whole number part. Therefore, the elevator can accommodate 9 persons weighing 75 kg each at the same time.
Gold Foil Experiment Discovery in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice
The gold foil experiment led to the discovery of the ____.
– A) nucleus
– B) neutron
– C) electron
– D) cathode ray
Correct Answer: A) nucleus
Detailed Explanation:
The gold foil experiment, conducted by Ernest Rutherford in 1909, played a crucial role in the discovery of the nucleus of an atom. In the experiment, alpha particles (positively charged particles) were directed at a thin sheet of gold foil. According to the prevailing model at the time, the Thomson model, it was believed that the positive charge in an atom was uniformly distributed, and electrons were scattered throughout, much like raisins in a pudding. However, the surprising result of the gold foil experiment was that most alpha particles passed through the gold foil without much deflection. This suggested that the majority of the atom is empty space. But, crucially, some alpha particles were deflected at large angles or even bounced back. Rutherford interpreted these unexpected results as indicating that the positive charge in an atom is concentrated in a tiny, dense nucleus at the center. The nucleus is where most of the mass is located. This discovery fundamentally changed the understanding of atomic structure and led to the development of the nuclear model of the atom, with electrons orbiting around the nucleus, in the context of the chemistry emsat practice. So, the correct answer is nucleus, as the gold foil experiment provided experimental evidence for the existence and location of the atomic nucleus.
Nucleus Composition in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice
Which particles are found in the nucleus of an atom?
– A) protons and neutrons
– B) protons and electrons
– C) neutrons and electrons
– D) protons
Correct Answer: A) protons and neutrons
Detailed Explanation:
The nucleus of an atom contains two types of subatomic particles: protons and neutrons. Protons: Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, and it defines the identity of the element. For example, all carbon atoms have six protons in their nucleus. Neutrons: Neutrons are neutral particles (having no charge) found in the nucleus alongside protons. They contribute to the mass of the nucleus without adding a charge. Neutrons help bind protons together through the strong nuclear force, helping to stabilize the nucleus. Together, protons and neutrons are tightly packed in the nucleus, while electrons orbit the nucleus in electron shells. The nucleus is the central, dense core of an atom, and it contains the vast majority of the atom’s mass, in the context of the chemistry emsat practice. So, the correct answer is protons and neutrons, as these are the particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Heat Removal and Phase Change in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice
The below graph for a substance being heated from – 50°C to 600°C.
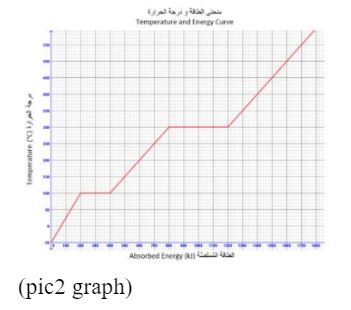
If 600 kJ of heat are removed from the substance when it is at 350°C, what will be the state and temperature of the substance?
– A) liquid at 250°C
– B) gas at 250°C
– C) solid at 200°C
– D) liquid at 200°C
Correct Answer: C) solid at 200°C
Detailed Explanation:
Within the context of the chemistry emsat practice, the information provided in the question indicates that 600 kJ of heat are removed from the substance when it is at 350°C. This suggests that the substance is undergoing a phase change, as the temperature remains constant during a phase transition. Solid at 200°C, this option implies that the substance is in a solid state at 200°C. Given that 600 kJ of heat is removed, this is consistent with the substance undergoing a phase change from a liquid to a solid. The temperature remains constant during this phase transition. So, as heat is removed and the substance changes from a liquid to a solid, the temperature would remain constant at the freezing (or melting) point. In this case, the freezing point is 200°C, so the substance is a solid at 200°C. Therefore, the correct answer is solid at 200°C.
Equilibrium Constant and Product Concentration in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice
The equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 1.5 × 10+⁵
X⇌Y
Based on the above information, the reaction at equilibrium will always have ____.
– A) large amount of product Y
– B) large amount of reactant X
– C) 75% product of Y and 25% reactant X
– D) 50% product of Y and 50% reactant X
Correct Answer: A) large amount of product Y
Detailed Explanation:
Within the context of the chemistry emsat practice, the equilibrium constant (K) for the reaction X⇌Y is given as 1.5 × 10+⁵.
The magnitude of the equilibrium constant (|K|) provides information about the position of the equilibrium:
If |K| is much greater than 1 (K ≫ 1), it indicates that the equilibrium favors the products. In this case, the concentration of the products at equilibrium will be relatively higher than the concentration of the reactants.
Given that K = 1.5 × 10⁵ is significantly greater than 1, it suggests that the equilibrium position strongly favors the products (Y). Therefore, at equilibrium, there will be a large amount of product Y compared to the reactant X.
So, large amount of product Y is the correct choice based on the given information about the equilibrium constant K.
Titrating Concentration in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice
A student conducted a titration by adding 12.0 mL of NaOH(aq) of unknown concentration to 16.0 mL of 0.15 M HCl(aq). What is the molar concentration of the NaOH(aq)?
– A) 0.2 M
– B) 2.0 M
– C) 0.15 M
– D) 2.4 M
Correct Answer: A) 0.2 M
Detailed Explanation:
To find the molar concentration within the context of the chemistry emsat practice, of NaOH (NaOH(aq)), we can use the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between NaOH and HCl:
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l)
From the balanced equation, we can see that the mole ratio between NaOH and HCl is 1:1. This means that the moles of NaOH used are equal to the moles of HCl reacted.
Given that the initial molar concentration of HCl (HCl(aq)) is 0.15 M and the volume is 16.0 mL (or 0.016 L), we can calculate the moles of HCl:
moles of HCl = molar concentration × volume
moles of HCl = 0.15M × 0.016L
moles of HCl = 0.0024 moles
Since the mole ratio is 1:1, the moles of NaOH used are also 0.0024 moles.
Now, we can find the molar concentration of NaOH (NaOH(aq)) using the volume of NaOH added (12.0 mL or 0.012 L):
molar concentration of NaOH = moles of NaOH ÷ volume of NaOH
molar concentration of NaOH = 0.0024 moles ÷ 0.012 L
molar concentration of NaOH = 0.2 M
So, the correct answer is 0.2 M.
Unveiling the Atom in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice – Matter:
What is the smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical properties?
– A) Molecule
– B) Atom
– C) Compound
– D) Ion
Correct Answer: B) Atom
Detailed Explanation:
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter and represent the smallest unit of an element that retains its unique chemical properties. Understanding this concept requires exploring the nature of elements and their basic constituents. Atom, signifies the foundational unit that embodies the characteristic properties of a specific element. This understanding is pivotal in grasping the essence of elemental behavior and forms the cornerstone of chemical knowledge in the context of the chemistry emsat practice.
Navigating Shared Bonds in chemistry emsat practice
- Multi-select – Bonding:
Which types of bonds involve the sharing of electrons? (Select all that apply)
– A) Ionic
– B) Covalent
– C) Metallic
– D) Pola
Correct Answer: B) Covalent, C) Metallic
Detailed Explanation:
Understanding the nature of chemical bonds is crucial in appreciating how atoms come together to form compounds. In this question, the focus is on bonds that involve the sharing of electrons. Covalent and Metallic, highlight bonds where electrons are shared. Covalent bonds involve a direct sharing of electrons between non-metal atoms, while metallic bonds involve the delocalized sharing of electrons in a metal lattice. This nuanced understanding is essential for navigating the intricacies of chemical bonding in the context of the chemistry emsat practice.
Unraveling A:B Mole Ratios in chemistry emsat practice
- Fill-in-the-Blank – Stoichiometry:
In the balanced chemical equation 2A+3B→4C2A+3B→4C, the mole ratio of A to B is:
Correct Answer: 2:3
Detailed Explanation:
Stoichiometry is a fundamental concept in chemistry that involves the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. In this particular question, the mole ratio between A and B is being explored in the context of the given balanced chemical equation:
Balanced Equation: 2A + 3B → 4C
The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation represent the mole ratios between the different species involved. In this equation:
The coefficient of A is 2.
The coefficient of B is 3.
The mole ratio of A to B is therefore expressed as 2:3. This signifies that for every 2 moles of A involved in the reaction, 3 moles of B are also involved, maintaining the stoichiometric balance required for the reaction to proceed correctly. Understanding mole ratios is crucial for performing stoichiometric calculations, determining limiting reactants, and predicting the quantities of products formed in a chemical reaction. In the context of the chemistry emsat practice, having a firm grasp of stoichiometry allows students to navigate complex reaction scenarios with confidence, ensuring accurate and insightful problem-solving skills in the realm of chemical equations and reactions.
Reaction Recognition in chemistry emsat practice
- Drag and Drop – Chemical Reactions:
Match the type of reaction with the given equation:
Equation:
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
Types:
Synthesis
Decomposition
Combustion
Replacement
Correct Match: Combustion (Drag and drop next to CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O)
Detailed Explanation:
The given equation CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O represents a combustion reaction. In combustion, a substance (in this case, the hydrocarbon CH₄) reacts with oxygen (O₂) to produce carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). Combustion reactions are characterized by the rapid combination of a fuel with oxygen, often resulting in the release of heat and light. This specific combustion reaction is commonly associated with the burning of methane (CH₄), a hydrocarbon, in the presence of oxygen. Understanding the specific type of chemical reaction based on the given equation is essential for categorizing reactions and predicting their behavior. This knowledge is particularly valuable in the chemistry emsat practice, where identifying reaction types is a fundamental skill for solving complex problems related to chemical transformations.
Energy Conservation in chemistry emsat practice
- Multiple Choice – Thermodynamics:
Which law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another?
– A) First Law of Thermodynamics
– B) Second Law of Thermodynamics
– C) Third Law of Thermodynamics
– D) Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
Correct Answer: A) First Law of Thermodynamics
Detailed Explanation:
The laws of thermodynamics are foundational principles governing the behavior of energy in physical systems. In this multiple-choice question, the focus is on the law that addresses the conservation of energy which is, First Law of Thermodynamics. This law is fundamental in understanding the conservation of energy and forms the basis for various thermodynamic processes. It implies that the total energy within a system remains constant, highlighting the principle that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can undergo transformations between different forms. In the context of the chemistry emsat practice, a solid grasp of the First Law of Thermodynamics is essential for analyzing and predicting energy changes in chemical reactions, providing a foundational understanding for more complex thermodynamic concepts.
Dynamic Equilibrium in chemistry emsat practice
- Multi-select – Equilibrium:
What factors affect the position of equilibrium in a reversible reaction? (Select all that apply)
– A) Temperature
– B) Pressure
– C) Concentration
– D) Catalyst presence
Correct Answers: A) Temperature, C) Concentration
Detailed Explanation:
Understanding the factors that influence the position of equilibrium in a reversible reaction is crucial in predicting how the system responds to changes. In this question, the focus is on the impact of various factors, Temperature and Concentration. Temperature directly influences the kinetic energy of particles and the rate of reactions, impacting the position of equilibrium. Concentration changes, on the other hand, prompt the system to adjust to maintain equilibrium by shifting towards the side with the lower concentration. This understanding is crucial in the context of the chemistry emsat practice, where predicting the effects of changes on the equilibrium position is a key aspect of mastering chemical reactions and their dynamic nature.
Double Bonds Decoded in chemistry emsat practice
- Fill-in-the-Blank – Hydrocarbons:
A hydrocarbon with a double bond between carbon atoms is called ____.
Correct Answer: Alkene
Detailed Explanation:
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting solely of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are classified into different types based on the type of bonds and structures they exhibit. In this question, the focus is on hydrocarbons with a specific type of bond, Alkene. An alkene is a type of hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). The presence of this double bond introduces a degree of unsaturation into the molecule. Alkenes are part of the larger family of unsaturated hydrocarbons, as opposed to alkanes, which are saturated hydrocarbons containing only single bonds between carbon atoms. The general formula for an alkene is CnH₂n, where n represents the number of carbon atoms. The double bond provides a site for chemical reactions, making alkenes versatile in organic chemistry. Understanding the nomenclature and structural features of hydrocarbons is essential in organic chemistry. In this case, recognizing that a hydrocarbon with a double bond between carbon atoms is termed an alkene is crucial. The term alkene provides specific information about the type of hydrocarbon and indicates the presence of a double bond, distinguishing it from other hydrocarbon classes. In the context of the chemistry emsat practice, familiarity with hydrocarbon nomenclature and classifications is fundamental for identifying and describing organic compounds, enabling students to navigate questions related to organic chemistry with confidence and precision.
Analytical Techniques in chemistry emsat practice
- Drag and Drop – Analytical Chemistry:
Arrange the following techniques in order of increasing mass resolution:
– Techniques: (Drag and drop to arrange)
– NMR Spectroscopy
– Mass Spectrometry
– Infrared Spectroscopy
– Gas Chromatography
Correct Order:
- Gas Chromatography
- Infrared Spectroscopy
- NMR Spectroscopy
- Mass Spectrometry
Detailed Explanation:
Analytical chemistry encompasses a variety of techniques for the identification and quantification of substances. The order of increasing mass resolution for the listed techniques is determined by their ability to separate and detect ions or molecules based on their mass-to-charge ratio or molecular weight. The correct order, from Gas Chromatography to Mass Spectrometry, represents an increasing trend in mass resolution. Gas Chromatography separates compounds based on their volatility and boiling points, while Mass Spectrometry provides the highest mass resolution, allowing for precise determination of the molecular weight of ions. This knowledge is crucial in analytical chemistry, aiding scientists in selecting the appropriate techniques based on their specific analytical needs and goals. In the context of the chemistry emsat practice, understanding the principles and applications of analytical techniques is fundamental for solving complex problems related to chemical analysis.
Particle Emissions in nuclear chemistry emsat practice
- Multi-select – Nuclear Chemistry:
Which particles can be emitted during radioactive decay? (Select all that apply)
– A) Alpha particle
– B) Beta particle
– C) Gamma ray
– D) Neutron
Correct Answers: A) Alpha particle, B) Beta particle, C) Gamma ray
Detailed Explanation:
Radioactive decay involves the transformation of unstable atomic nuclei into more stable configurations. This process often includes the emission of particles and/or electromagnetic radiation. Alpha particle, Beta particle, and Gamma ray, can indeed be emitted during various types of radioactive decay processes. Understanding the characteristics of each particle and their roles in nuclear reactions is fundamental in nuclear chemistry. In the context of the chemistry emsat practice, this knowledge is essential for tackling questions related to nuclear processes and their implications for the stability of atomic nuclei.
pH Proficiency in chemistry emsat practice
- Drag and Drop – Fill-in-the-Blank:
Match the pH scale values with their corresponding acidity levels:
– Values: (Drag and drop to match)
– 0-3
– 4-6
– 7
– 8-14
– Acidity Levels:
– Very acidic
– Mildly acidic
– Neutral
– Basic
Correct Match:
– 0-3: Very acidic
– 4-6: Mildly acidic
– 7: Neutral
– 8-14: Basic
Detailed Explanation:
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale that measures the acidity or basicity of a solution. Each pH value corresponds to a specific concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the solution. The correct matches illustrate the correlation between pH values and the acidity or basicity of solutions. Understanding the pH scale is crucial in determining the nature of a solution and its potential impact on chemical reactions or biological systems. In the context of the chemistry emsat practice, this knowledge is fundamental for interpreting experimental results and making informed predictions about the behavior of different substances in various environments.
Strategies for chemistry emsat practice success with ELMADRASAH.COM
- ELMADRASAH.COM ensures a solid understanding of foundational concepts in chemistry, such as atomic structure, chemical bonding, and stoichiometry, in order to provide you with comprehensive resources for chemistry emsat practice.
- Emphasizing the significance of a well-rounded education, ELMADRASAH.COM offers an EmSAT Chemistry Practice Test to further strengthen your grasp of essential chemical principles for your chemistry emsat practice.
- Regular chemistry emsat practice with ELMADRASAH.COM EmSAT Chemistry Sample Questions helps reinforce your understanding and improves your problem-solving skills.
- ELMADRASAH.COM offers you a time management practice for chemistry emsat practice by helping you set a realistic time limit for each question in the EmSAT Chemistry Practice Test, this will prepare you for the time constraints during the actual exam.
- After attempting ELMADRASAH.COM EmSAT Chemistry Sample Questions, we review your answers, and help you to understand any mistakes you made, which help you in identifying your weak areas for a further chemistry emsat practice study.
Success in the EmSAT Chemistry Practice Test requires a combination of conceptual understanding and effective problem-solving skills, as well as, for the actual exam. By mastering the top 10 ELMADRASAH.COM EmSAT Chemistry Sample Questions provided, you can enhance your preparation and approach the exam with confidence. Remember to practice consistently and manage your time wisely to reinforce your knowledge. Good luck on your chemistry emsat practice journey!